Chemosphere 350 (2024), 141182
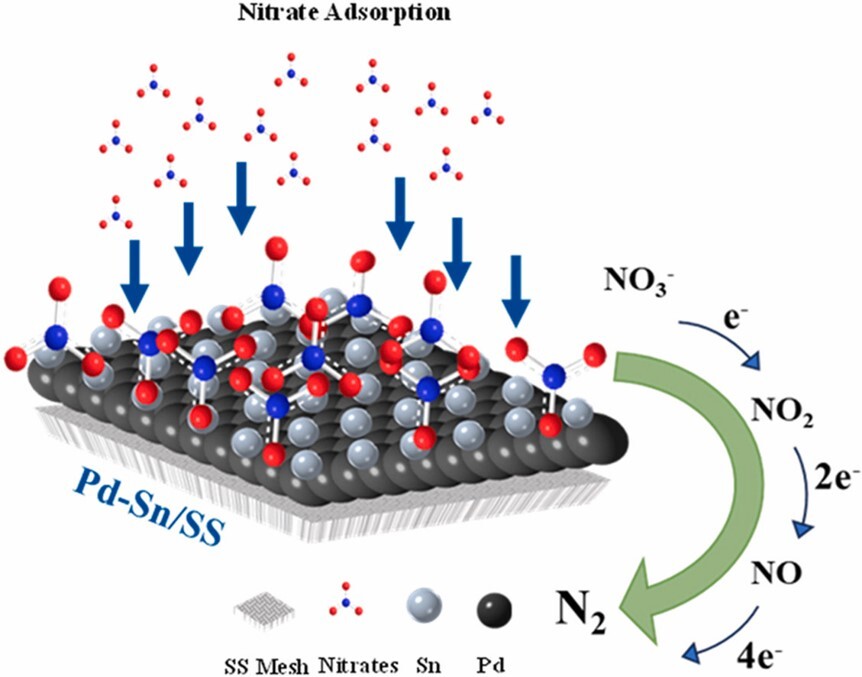
Nitrate is recognized as a highly impactful water contaminant among various pollutants in water. To address the ever-growing demand for water purification, this work investigates the bimetallic palladium (Pd) and tin (Sn) catalysts, which are electrochemically deposited on stainless steel mesh support (Pd–Sn/SS) for the selective conversion of harmful nitrate (NO3−) into benign nitrogen (N2) gas. Results indicate that the bimetallic composition in Pd–Sn/SS electrodes substantially influenced the reaction route for nitrate reduction as well as the performance of nitrate transformation and nitrogen selectivity. It is found that the electrode prepared from Pd:Sn = 1:1 (mole ratio) demonstrates an outstanding nitrate conversion of 95%, nitrogen selectivity of 88%, and nitrogen yield of 82%, which outperform many reported values in the literature. The electrochemically synthesized bimetallic electrode proposed herein enables a new insight for promoting the reactivity and selectivity of nitrate reduction in water.

